Rhino Mouse Acne model
Overview
Introduction
Rhino mouse acne model has been useful in assessing the comedolytic activity of drugs/compounds (i.e. retinoids)
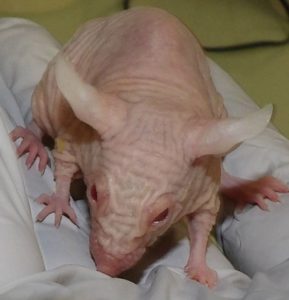
Phenotype Hrrh/Hrrh is due to an autosomal recessive mutation in the hairless (hr) gene
In Rhino mice, utriculi are derived from the infundibular zone of the initial follicular units, and are histologically similar to comedones
Protocol summary
Rhino mouse strain animals with application of compounds / new drugs on back skin
Histology evaluation on skin of utriculi (principal efficacy endpoint)
Evaluation of in vivo / ex vivo / analysis as secondary efficacy endpoints
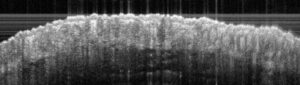
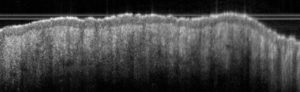
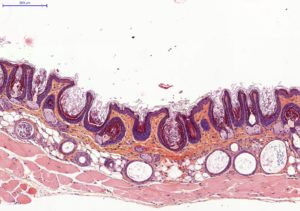
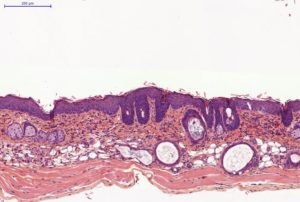
Typical results
Typical results obtained with this model are presented below:
Rhino Mouse Acne model / Detailed protocol
Age: Supplier dependent (generally from 8 to 12 weeks)
Gender: M and/or F / Supplier dependent
Randomization on age + gender at reception
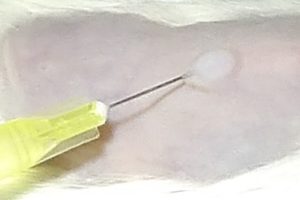
Application of dermatological pharmaceutical products
Ready to use formulations / Formulation screening on request
Intra-dermal route (i.e. Medical Devices or injectable drugs)
Topical route / Reference drugs: Isotretinoin or Adapalene or Bexarotene
Oral route / Reference drug: Isotretinoin
Treatment duration: 2-3 weeks
Evaluation of clinical macroscopic signs
Body weight / General behavior
Skin thickness / Caliper (back skin)
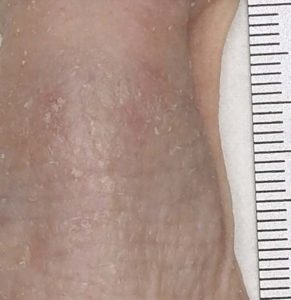
Skin macroscopic description (back skin):
- Scaling (skin dryness)
- Erythema (skin redness)
- Other macroscopic skin observations
- Sebum production using sebumeter
In vivo imaging
Macroscopical observation: Digital pictures of back skin
Sub-macroscopical exploration: Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) for epidermis thickness measurement
Ex vivo imaging
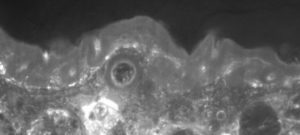
Histology on back skin slices obtained from paraffin blocks or frozen blocks
HES (Hemalun-Eosin-Safran) / Overall evaluation of efficacy (utriculi / sebaceous glands)
Immuno-histochemistry
Ki67 staining for keratinocyte / fibroblast / sebocyte proliferation index calculation
Other stainings on request
Other ex vivo imaging techniques of interest:
3D reconstruction of sebaceous glands for volume evaluation
Light Sheet microscopy (in collaboration)
MALDI imaging (in collaboration)
Samples collection and analysis
Plasma and skin sampling, sebum sampling (surface skin lipids (SSLs) analysis)
Cytokines analysis in skin extract / plasma (terminal sampling))
– Single ELISA assay (1-2 cytokines)
– Multiplexed analysis of cytokines (>2 cytokines)
Sebum lipidomics collected in vivo (repeated sampling) or at termination for evaluation sebum composition:
– Fatty acids
– Sterols
– Cholesterol
– Wax esters
– Triglycerides
– Cholesteryl esters
Rhino Mouse Acne model / Conclusion
Rhino mouse model is a first intention model, fast and reproducible.
6 animals per group are generally sufficient to underline anti-acne effect of new therapeutics (based on difference of at least 20 to 30% of utriculi surface).
This model is well adapted for anti-seborrheic new drugs testing.
Cautions to be taken on this model :
Use of previously untested excipients should be avoid as they could cause false positive, false negative or local irritation
Formulation physico-chemistry must be well known (pH, osmolarity, etc…)
Drug pharmacokinetics / ADME / transcutaneous passage should be known to optimize dosing.
Do not hesitate to contact us if you need more information or a quotation on this model.
Bibliography of interest
- Seiberg, M., et al. The effects of trypsin on apoptosis, utriculi size, and skin elasticity in the Rhino mouse. J. Invest. Dermatol. 109, 370–376 (1997).
- Hsia, E., et al. Effects of topically applied acitretin in reconstructed human epidermis and the rhino mouse. J. Invest. Dermatol. 128, 125–30 (2008).
- Benavides, F., et al. The hairless mouse in skin research. J. Dermatol. Sci. 53, 10–18 (2009).
- Nieves, N. J., et al. Identification of a unique subset of 2-methylene-19-nor analogs of vitamin D with comedolytic activity in the rhino mouse. J. Invest. Dermatol. 130, 2359–67 (2010).